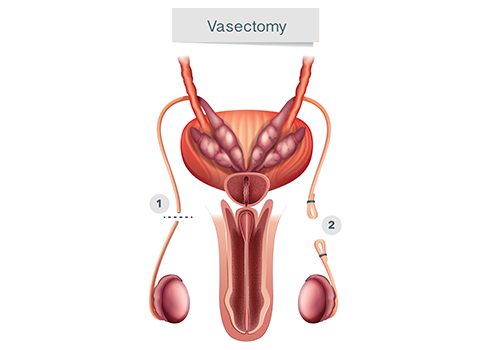
During vasectomy, each vas deferens (the two tubes that move sperm) is sealed off. This blocks sperm from reaching the semen that is ejaculated. After a vasectomy, the testicles still make sperm but the sperm are absorbed by the body.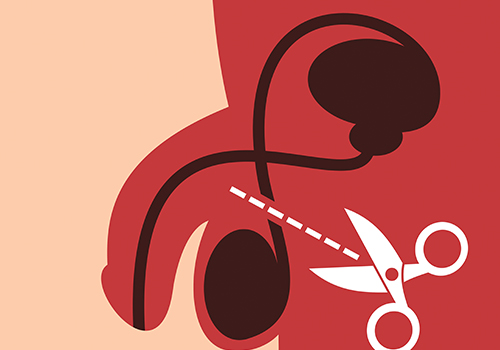
Vasectomy is a minor surgical procedure that should take about 20 minutes. Your doctor can perform a vasectomy in the office, at a surgery center, or at the hospital on an outpatient basis. Local anesthesia is usually used, so you will be awake, but should not feel any pain. If you’re anxious about the surgery, your physician can give you medication to reduce your anxiety before surgery.
With a standard vasectomy, your urologist makes one or two small incisions in the scrotum. One vas deferens tube is cut and tied or sealed with heat. The tube is replaced inside the scrotum. The procedure is then repeated on the other side. Then, the skin is closed with stitches that dissolve and do not have to be removed.
A no-scalpel vasectomy is another option although all vasectomy procedures require that a cut be made in the skin. In this procedure, a small clamp is used to puncture the skin instead of a scalpel. Then each vas deferens is lifted out, cut, sealed, and put back in place. A no-scalpel vasectomy works just as well as a standard vasectomy and there is a similar risk of bleeding, discomfort and other complications.