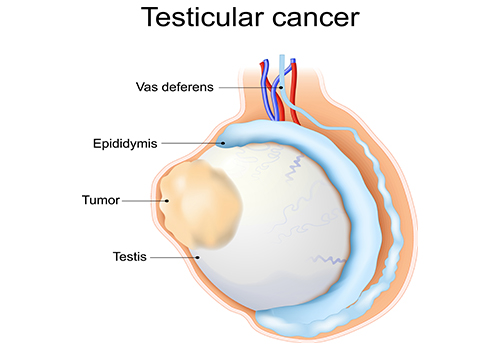
Testicular cancer is the most common cancer among men age 18 to 35. About 8,800 men will be diagnosed with testicular cancer in the U.S.
The testicles (also known as testes) are the two oval glands contained in a sac below the penis. They make sperm and the male sex hormone testosterone. While some patients with congenital conditions, such as an undescended testis, may be at higher risk, there is no known way to prevent testicular cancer. That’s why it’s important for young men to know the symptoms of the disease and get any concerns checked out by a physician right away.
Our specialists are expert in diagnosing and treating this type of cancer employing the most modern and non-invasive approaches to eradicate disease. We work with a multidisciplinary treatment team, including oncologists and radiation specialists to provide comprehensive education and develop an individualized treatment plan tailored to each patients’ priorities, disease type and stage.
 There are several factors that can increase your risk of testicular cancer, including:
There are several factors that can increase your risk of testicular cancer, including: Usually, the first treatment is surgery to remove the testicle. For stage I patients, this may be the only treatment that is needed. Patients will then be followed closely by his physician with blood tests and scans to check for a return of the cancer. Stage II and III patients may need surgery to remove affected lymph nodes and may also need chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or removal of tumors that have spread farther.
Usually, the first treatment is surgery to remove the testicle. For stage I patients, this may be the only treatment that is needed. Patients will then be followed closely by his physician with blood tests and scans to check for a return of the cancer. Stage II and III patients may need surgery to remove affected lymph nodes and may also need chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or removal of tumors that have spread farther.
