Table of Contents
Symptoms
Epididymitis can be either acute, meaning it lasts for six weeks or less, or chronic, which lasts for six weeks or more. Symptoms for acute epididymitis often come on quickly and may be associated with sudden inflammation, swelling and pain. Acute epididymitis may also include inflammation of the testes (orchitis or epididymo-orchitis). Chronic epididymitis develops more slowly and is typically accompanied by a dull, achy pain.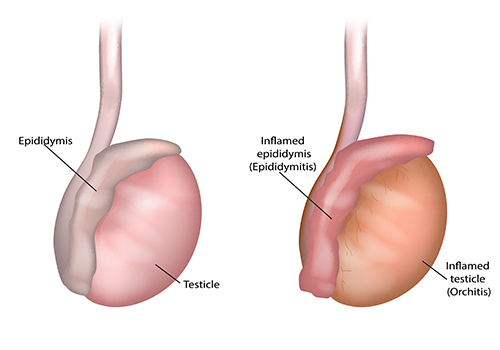
Symptoms to watch out for include low-grade fever, enlarged lymph nodes in the groin, urgent or frequent urination, abnormal discharge from the penis, or blood in the semen.
Epididymitis is also typically accompanied by pain and/or pressure in the pelvic area and testicles during sexual intercourse, urination or bowel movements. Also watch out for redness, tenderness or warmth in the scrotum.
Causes
Epididymitis can happen to individuals of all ages but is more common in males aged 14 to 35. It is typically caused by a bacterial infection or a sexually transmitted infection. Gonorrhea and chlamydia are the most common causes of sexually transmitted epididymitis as they cause an infection in the urethra which can sometimes travel down the vas deferens to the epididymis or testes and cause infection. Urinary tract or prostate infections, tuberculosis, and other non-sexually transmitted diseases can similarly travel from the urethra to the epididymis causing epididymitis.
Treatments
Treatment for epididymitis is dependent on the underlying infection. Treatment for a bacterial infection often includes medication such as antibiotics, pain medication, and anti-inflammatory medication. Doctors will often suggest bed rest, cold packs, and avoiding heavy lifting or straining. It can often take a week to several weeks-long course of antibiotics to eliminate the infection. It is important to complete the entire course of antibiotics.
Occasionally, complications with more severe epididymitis arise which can include puss-filled infections or abscesses in the scrotum. If the condition spreads from the epididymis to the testes, the condition is called epididymo-orchitis. Occasionally, severe epididymitis may be associated with reduced fertility. If no other treatments prove successful, surgery may become an option. In these circumstances, all or part of the epididymis and, in rare cases, the testicle may be removed and any physical defects that may be causing the infection will be corrected.

