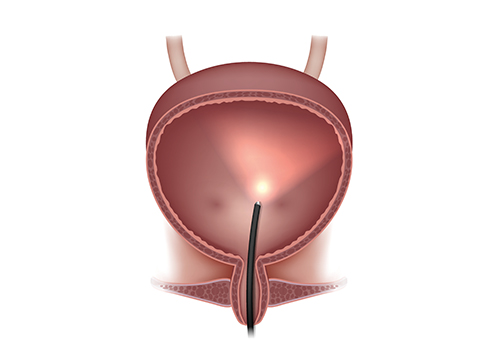
Cystoscopy is a procedure with a fiber optic telescope that allows us to visually inspect the inside of your urethra and bladder.
This study is often performed in people who have blood in the urine, difficulty emptying the bladder, bladder stones, urethral strictures or infections. We can determine if there are any abnormalities including narrowed areas (strictures or contractures), outpouchings called diverticula or an enlarged prostate in males. Inflammation, bleeding, stones, and tumors can also be identified. This study also allows us to evaluate the muscle (sphincter) which regulates the outflow of urine from your bladder.